We’ll start with a working example that displays building footprints in a vector layer over a base layer. Open your text editor and save the following as map.html in the root of your workshop directory:
<html>
<head>
<title>My Map</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="openlayers/theme/default/style.css" type="text/css">
<style>
#map-id {
width: 512px;
height: 256px;
}
</style>
<script src="openlayers/lib/OpenLayers.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Map</h1>
<div id="map-id"></div>
<script>
var medford = new OpenLayers.Bounds(
4284890, 253985,
4288865, 257980
);
var map = new OpenLayers.Map("map-id", {
projection: new OpenLayers.Projection("EPSG:2270"),
units: "ft",
maxExtent: medford,
restrictedExtent: medford,
maxResolution: 2.5,
numZoomLevels: 5
});
var base = new OpenLayers.Layer.WMS(
"Medford Streets & Buildings",
"/geoserver/wms",
{layers: "medford"}
);
map.addLayer(base);
var buildings = new OpenLayers.Layer.Vector("Buildings", {
strategies: [new OpenLayers.Strategy.BBOX()],
protocol: new OpenLayers.Protocol.WFS({
version: "1.1.0",
url: "/geoserver/wfs",
featureType: "buildings",
featureNS: "http://medford.opengeo.org",
srsName: "EPSG:2270"
})
});
map.addLayer(buildings);
map.zoomToMaxExtent();
</script>
</body>
</html>
Open this map.html file in your browser to see orange buildings over the base layer: http://localhost:8080/ol_workshop/map.html
With a basic understanding of styling in OpenLayers, we can create an OpenLayers.StyleMap that displays buildings in different colors based on the size of their footprint. In your map initialization code, replace the constructor for the buildings layer with the following:
var buildings = new OpenLayers.Layer.Vector("Buildings", {
strategies: [new OpenLayers.Strategy.BBOX()],
protocol: new OpenLayers.Protocol.WFS({
version: "1.1.0",
url: "/geoserver/wfs",
featureType: "buildings",
featureNS: "http://medford.opengeo.org",
srsName: "EPSG:2270"
}),
styleMap: new OpenLayers.StyleMap({
"default": new OpenLayers.Style({
strokeColor: "white",
strokeWidth: 1
}, {
rules: [
new OpenLayers.Rule({
filter: new OpenLayers.Filter.Comparison({
type: OpenLayers.Filter.Comparison.LESS_THAN,
property: "shape_area",
value: 3000
}),
symbolizer: {
fillColor: "olive"
}
}),
new OpenLayers.Rule({
elseFilter: true,
symbolizer: {
fillColor: "navy"
}
})
]
})
})
});
Save your changes and open map.html in your browser: http://localhost:8080/ol_workshop/map.html
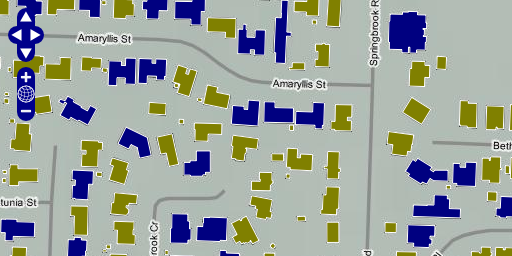
Buildings colored by footprint area.